 The corporation board of stakeholders
The corporation board of stakeholders
Companies with stakeholder boards maximize positive society impact over maximum company profits.
To conclude a series of articles I have written on stakeholders, I would like to offer a suggestion. The ideas partly came to me while reading the book, Conscious Capitalism by John Mackey and Raj Sisodia. They define categories of stakeholders and start with this statement: “Capitalism, done consciously, is the most powerful system for uplifting humankind to unimaginable levels of prosperity, peace, and happiness.” It is performed by “value-based and purpose-driven” capitalism. They believe that top management must be dedicated to their cause.
Fitting in nicely with the Open Organization Principles of Transparency, Inclusivity, Adaptability, Collaboration and Community, I wanted to add my suggestion to put top management to the stakeholder test.
Stakeholder Commitment
First, confirm stakeholder commitment to that cause. We hear a lot about being accountable these days, but who is managing (or supervising) that accountability to the stakeholders? Many companies have full-time compliance officers, but do they all collaborate with each other and support each other?
To find out if a company is really committed to their stakeholders, ask this question to find out: Does the company have a “Stakeholder” board, as in the title of this article? For example, notice the below example:
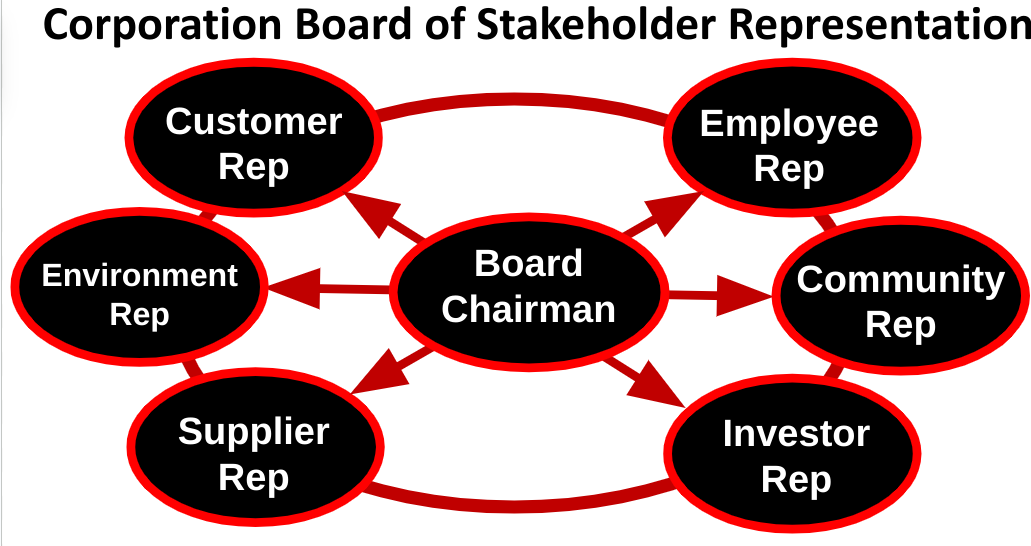
Companies with stakeholder boards might be part of what is called B (benefit) Corporations. They maximize positive society impact over maximum company profits.
If it has a board, who is in charge of each stakeholder, and what is the budget for each? What are the stakeholder achievement measurements?
If there isn’t a single stakeholder group, ask how the stakeholder representatives collaborate with and support each other.
If there is no stakeholder representation at all, then the company is more than likely only concerned with its own profitability and nothing else. They only talk about stakeholders as an idea, but have no execution plan.
Stakeholder representation role
For more detail, each of the six represents an entire group’s concerns. These are full-time positions, paid from allotting 1% of net profits annually - similar to the 1% of profits that go to the Google Foundation each year from Google’s net profits. These stakeholders have the drive to make a positive global impact and still be profitable. This role to serve stakeholders is explained and presented in a written agreement in which the representative candidate signs.
Stakeholder Board position and categories
The Stakeholder Board is written right in the company charter and is provided a yearly budget for customer relations, employee relations, environment relations, supplier relations, community relations and investor relations. This group is to decide the company’s purpose and create a success strategy for all of them.
In their book, Mackey and Sisodia say other representatives should be included to determine their company purpose, including: senior company leaders, board members, team members, customers, investors, suppliers, and members of the community. They recommend this group sets company goals, targets, indicators and measurements. To ensure that everyone knows what is to be achieved, it could be detailed similar to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) - but on a company basis. I would recommend a chairman and only six representatives to make the proposal easier to execute.
All stakeholders on this board must share two desires:
Desire to serve others - They must have a strong desire to serve those they represent and enjoy seeing the success of others. These people have strong empathy for others and want them to prosper.
Desire to be respected - They have a desire to be respected and to benefit from what they have offered all stakeholders, which compels them and others to serve each other.
Board member descriptions
Let me define more clearly the roles of each of these stakeholder board members, including one person heading the board:
1. Board Chairman’s Role & Responsibilities
The chairman reports to company management. He understands and is qualified to evaluate the entire organization’s ecosystem, including the supply chain, its impact on the environment and its impact on the surrounding community. He must know the relationships between all stakeholders and how they impact on the greater social and natural environment.
As chairman, he holds quarterly meetings and makes sure all representatives’ perspectives are presented, appreciated and heard. Their concerns are all exposed, evaluated and acted on if adjustments need to be made. He also makes sure all the representatives talk to each other to collaborate, discuss and come up with ways each can be further helpful to each other. If there are conflicts between stakeholders, he helps resolve them. This person is probably a professional or consultant in stakeholder management.
He helps the board develop stakeholder measurable targets and doable performance standards. Each representative is responsible for evaluating those targets and standards. Then, the members report their results at the quarterly board meetings.
He prepares a document of all stakeholder’s interdependent performance, their impact on each other and all stakeholder board satisfaction levels yearly to company management. Based on that report, he recommends stakeholder representative activities and goals for the next year and asks for the estimated budget required.
2. Customer Representative’s Role & Responsibilities
Is the market being served to its satisfaction? What could be made available that is not? An employee representative should be able to answer that question.
This representative is probably a customer satisfaction consultant or someone who fully knows the markets the company serves. He must desire the success of the company and customer satisfaction. He asks how the employees, environmental improvements, investors, suppliers and community members can improve customer service. If this representative can find things that the customer doesn’t even know about but could joyfully use, great satisfaction can be created, to the level of testimonials to others.
This representative’s job is to learn the feelings of the customers, particularly major customers, and look where customer-company relationships can be improved. He must do that while listening to and respecting all other stakeholder representative’s positions.
3. Employee Representative’s Role & Responsibilities
The employees must be motivated and proud of the company they work for. Also, they must feel they are rewarded when the company does well and are willing to take cuts if it will keep the company in business. Therefore, this representative should speak for the concerns of all workers, including people in management, as they are also employees.
Are managers getting huge bonuses but the frontline staff getting laid off? This employee representative should answer that question and resolve any concerns. This person is probably a professional or consultant in personnel management and knows how to motivate workers, including managers, on stakeholder value and company purpose.
This representative must desire employee satisfaction as well as company success. He could collaborate with other stakeholders by asking how environmental improvements, investors, suppliers and community members can improve employee working conditions. If the employees, particularly long service employees, think their compensation is fair and reasonable, and can work in an environment which provides a way to learn and develop, and have autonomy in how they can excel in their work and can work on assignments they consider valuable to society, they will be so motivated that they will represent the company well to other stakeholders.
This representative’s job is to evaluate compensation fairness - whether salaried or commissioned, hourly or monthly, high ranking or junior staff. Does everyone feel this is appropriate? Are improvements needed? He must answer these questions, while listening to and respecting all other stakeholders.
4. Supplier Representative’s Role & Responsibilities
Are the suppliers treated fairly by the company? Do they do joint research with the company?
This representative must desire the success of the company and all suppliers. He could collaborate with other stakeholders by asking how the customers, employees, environmental improvements, investors and community members can improve supplier’s concerns. Is innovative, joint development possible? By sharing information about their customers to suppliers, does the company collaborate with key suppliers to offer products for the future?
The supplier representative evaluates how trusted and closely all who provide service or goods to the company feel about the company and its purpose. He looks at how well the company’s purpose and the major supplier’s purpose match each other. The representative must do that while listening to and respecting all other stakeholder representative’s positions.
5. Community Representative’s Role & Responsibilities
Is the neighborhood happy that the company is in the community? If yes, why? If no, why not? What should the company be doing in the community?
This representative must desire a good relationship with the neighboring areas and indirect communities like all the surrounding schools, hospitals, community centers, chamber of commerce, Rotary and Lions clubs, shopping areas, parks, etc. He could collaborate with other stakeholders by asking how the customers, employees, environmental improvements, investors and suppliers can improve the local community.
The community representative evaluates how closely the neighborhood and surrounding areas connect to the purpose of the company. He tries to find the needs of the major community and how the company can help address those issues, as he wants the community and employee family members to prosper in their community.
Are all stakeholders proud of what the company is doing for the community? Does it raise their morale, or are they ashamed of how the company impacts on the community? Does the company have a charitable foundation for community improvement projects that all stakeholders are proud of? This representative is to make sure all stakeholders know that the company is donating to society. Also, he could ask all stakeholders to support company volunteer activities.
When there is a crisis in the community, does the company get involved? Does it provide support where it can? Also, do company decisions adversely influence the local community and does the company take that influence into consideration? This representative must make that impact as visible as possible, so the company will act appropriately to best serve the community as well as themselves.
6. Environment Representative’s Role & Responsibilities
This representative must speak for the environment which is impacted by the company directly first. Also, this person addresses any indirect impact the company has generally on global climate issues.
Is the company improving the environment by its activities? Or, is it harming the environment and indirectly the overall planet? Is the company transitioning to clean carbon-free energy sources? Does the company have active waste and resource/energy use reduction, reuse or recycling programs to protect the environment that people would be proud of? These activities could be both cost saving for the company, and improving the environment?
This representative is probably a professional or consultant on environmental issues and material waste reduction procedures, and has studied the impact companies have on the environment. He might have worked with suppliers regarding material waste. Furthermore, he must desire the success of the company, as well as protecting the environment directly and indirectly. Moreover, he could collaborate with other stakeholders by asking how the employees, customers, investors, suppliers and community members can participate in addressing environmental concerns.
The environmental representative evaluates how the company impacts on the direct and indirect natural environment. He studies any of the company’s major waste discharges, nearby pollution, fossil fuel use, greenhouse gas emissions, work safety, environmental compliance, and wasteful material utilization.
Are all stakeholders proud of what the company is doing toward the environment, or ashamed of what they are doing? He finds out and reports his findings to the Stakeholder Board, offers recommendations and works on action plans if need be.
7. Investor Representative’s Role & Responsibilities
As they are paid last among all stakeholders, investors will ask if the company is investing in worthwhile and sustainable projects. Are they proud of what their investments are achieving? Is the company kept viable to invest in the future? A company is like the human body. It needs food, but a person doesn’t live just to eat. The goals of his life are different. To have a prosperous future, companies need profits, but that should not be their main goal. What they do is, and those activities should result in profits.
This person is on the Board of Directors and reports to them. His main assignment is to convince all Board of Directors, including the Chairman of the Board, that the culture of the company believes that all other stakeholders have as much or more importance than just profits. With that value balance, profits might even be greater than if shareholder value was most important.
He believes that stockholders that don’t believe in the company's purpose should not invest in the company. He believes that far more investors that believe in what the company wants to achieve will be attracted to invest. The investor representative believes that profits are not a goal. They are only the result of successfully achieving the purpose of the organization. If the attention is placed on the company purpose, interestingly, the profits in the long-term will most likely be higher than if all their attention was short-term profits.
The company purpose must be continually presented and updated, so investors fully know the organization's mission. No, short-term investors, who heavily rely on quick profit analyst suggestions, should be welcome. Analysts mostly study financial data and not company contribution to society. The representative evaluates how closely the major investors believe in the purpose of the company and tries to find ways to increase that belief. He must do that while listening to and respecting all other stakeholder representative’s positions.
Stakeholder value generates profits
In their book, Conscious Capitalism, John Mackey and Raj Sisodia give many examples, case studies and research supporting the idea that by positively maximizing social and environmental impact, there will be higher profits.
One might think that if a company spent more money and energy on outside of company stakeholders - like customers, suppliers, environment or their community - the investors would suffer great losses. Yet according to many studies - such as those presented in another book, Firms of Endearment, How world-class companies profit from Passion and Purpose - that is not the case. Even the investors benefit, and that is why having a Board of Stakeholders is so important.
